Waste to Energy Transformation Technology
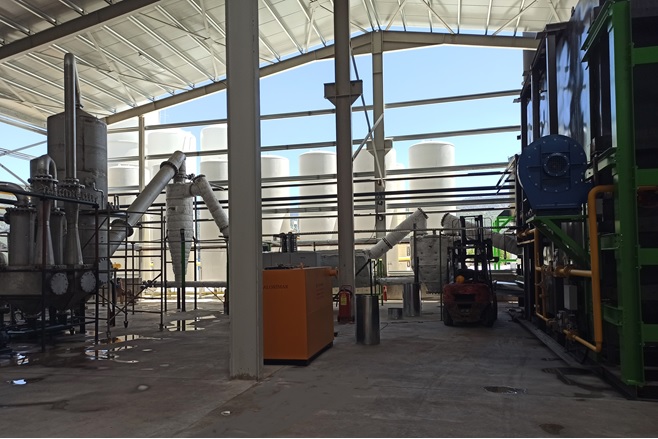

Waste to Energy Transformation Technology
Types of Wastes
Municipal solid waste
Agricultural Wastes (Palm waste, cacao waste, cow manure, corn waste etc.)
Forest Wastes (Tree barks, Tree roots, wood Chips etc.)
Industrial Wastes (car tires, industrial oils, petroleum wastes, etc.)
Biomass is converted to energy through various processes, including:
Direct Combustion
Direct combustion is the most common method for converting biomass to useful energy. All biomass can be burned directly for heating buildings and water, for industrial process heat, and for generating electricity in steam turbines.

Chemical conversion to produce liquid fuels
A chemical conversion process known as transesterification is used for converting vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), which are used to produce biodiesel.
Biological Conversion to Produce Liquid and Gaseous Fuels
Biological conversion includes fermentation to convert biomass into ethanol and anaerobic digestion to produce renewable natural gas.
Ethanol is used as a vehicle fuel. Renewable natural gas also called biogas or biomethane is produced in anaerobic digesters at sewage treatment plants and at dairy and livestock operations
Thermochemical conversion to produce solid, gaseous, and liquid fuels
Thermochemical conversion of biomass includes pyrolysis and gasification. Both are thermal decomposition processes in which biomass feedstock materials are heated in closed, pressurized vessels called gasifiers at high temperatures.